About¶
The Algorithm¶
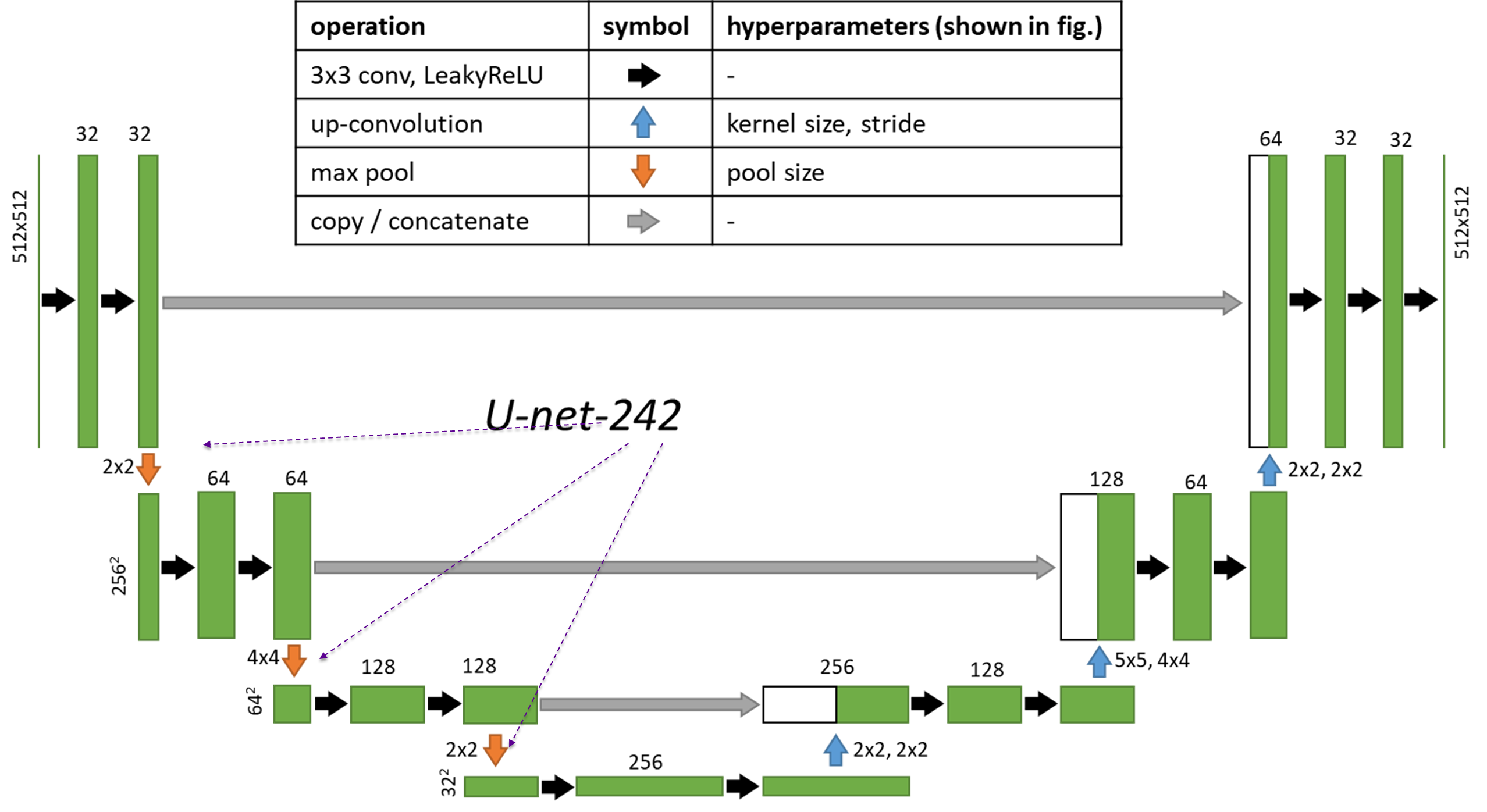
fCNN architecture¶
CTSegNet deploys unique Unet-like models trained with focal loss to provide accuracy with reduced number of convolutional layers. The methodology and performance metrics are discussed in [].
Here is an example architecture that you can build using the model_utils sub-module in CTSegNet. We will refer to it as Unet-242 because of the 2-4-2 implementation of pooling layers.
What is unique about CTSegNet?¶
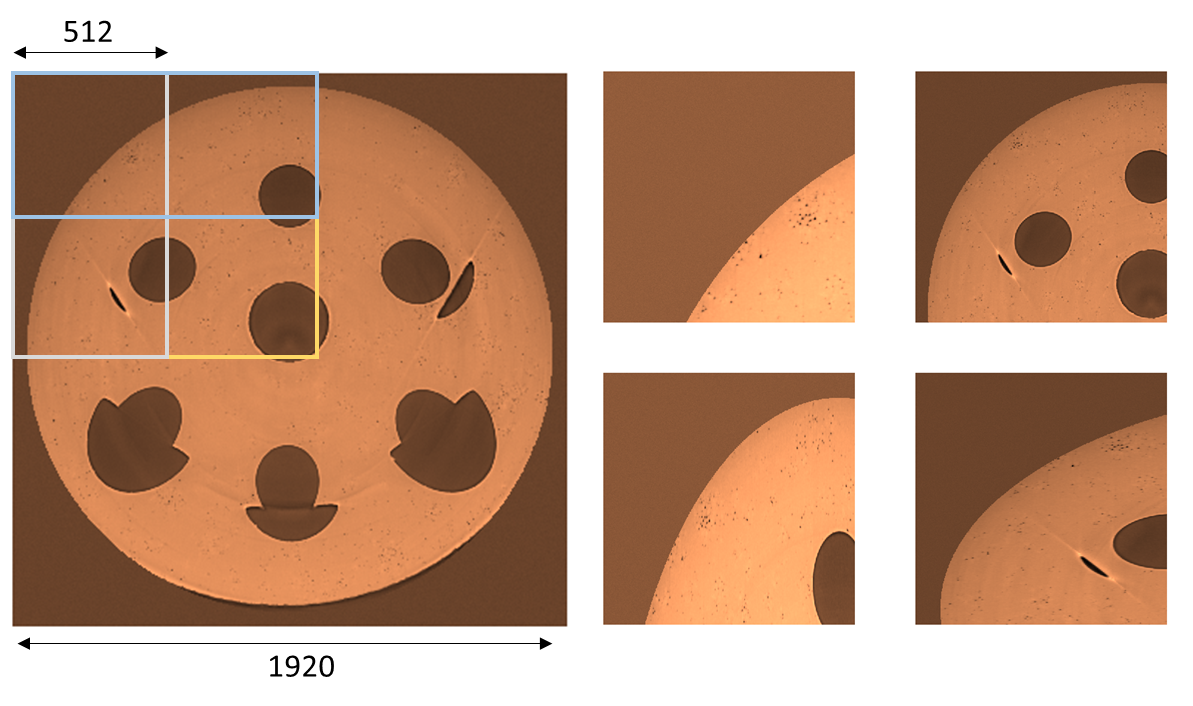
While Unet-based segmentation is now commonplace, it is primarily limited to 2D data since 3D convolutional layers require prohibitively large GPU memory during training. Our approach efficiently exploits 2D fCNNs for 3D segmentation. You can generate multiple 3D masks by slicing along any axis, and choose a patching strategy based on the resolution-to-context trade-off in your CT data. For an fCNN with input/output images sized 512x512, you can make patches in several ways. This a slice drawn from a scan of a gasoline injector along the transverse plane.
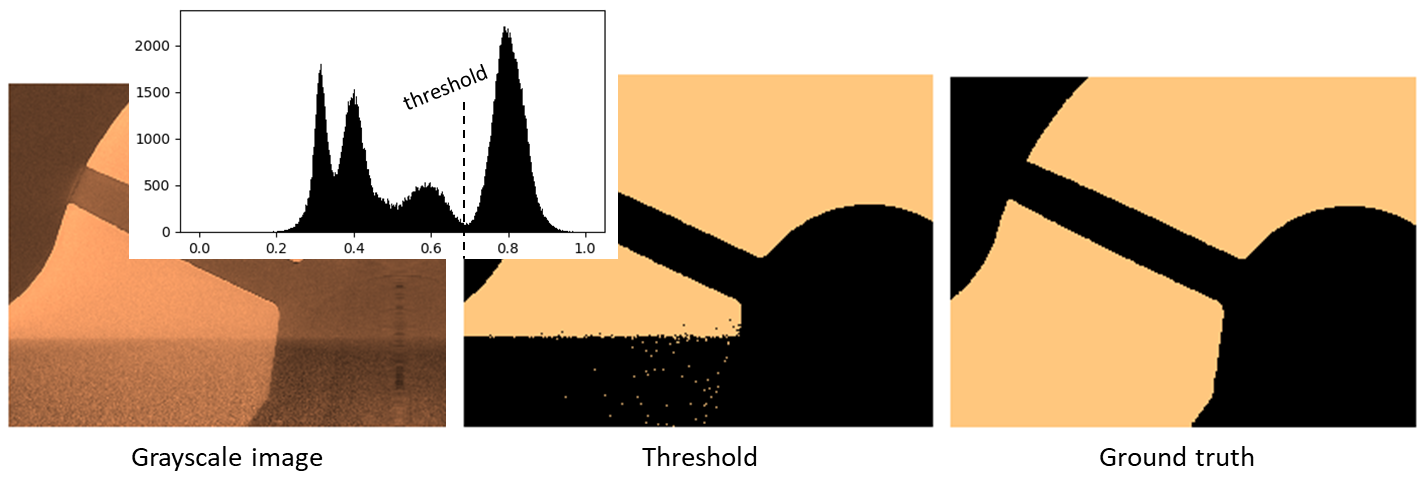
An ensemble vote from several 3D segmentations maps yields near voxel accuracy in many cases, where thresholding just won’t work. Here’s an example of a band-like artifact from restricted field-of-view in a CT scan (sagittal plane is shown).
The data_utils.data_io module contains the DataFile class, which enables fast and memory-efficient slicing using hdf5 format so you can visualize and segment 100GB+ datasets from your workstation. With this, you can segment only parts of your data or test models on slices of your data, with a few lines of code. Tiff format is also supported but with limited functionality.
Tell me more¶
Read our paper at [] or contact me at: atekawade [at] anl [dot] gov